Corruption in North Africa (a US perspective)
Introduction
The United States State Department’s Country Reports on Human Rights Practices (“country reports”) strive to provide a factual and objective record on the status of human rights worldwide. The 2021 country reports were published on 12 April 2022.
Section 4 of the country reports provides an assessment of Corruption and Lack of Transparency in Government which addresses the extent to which a country’s law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials and the level of implementation of these laws.
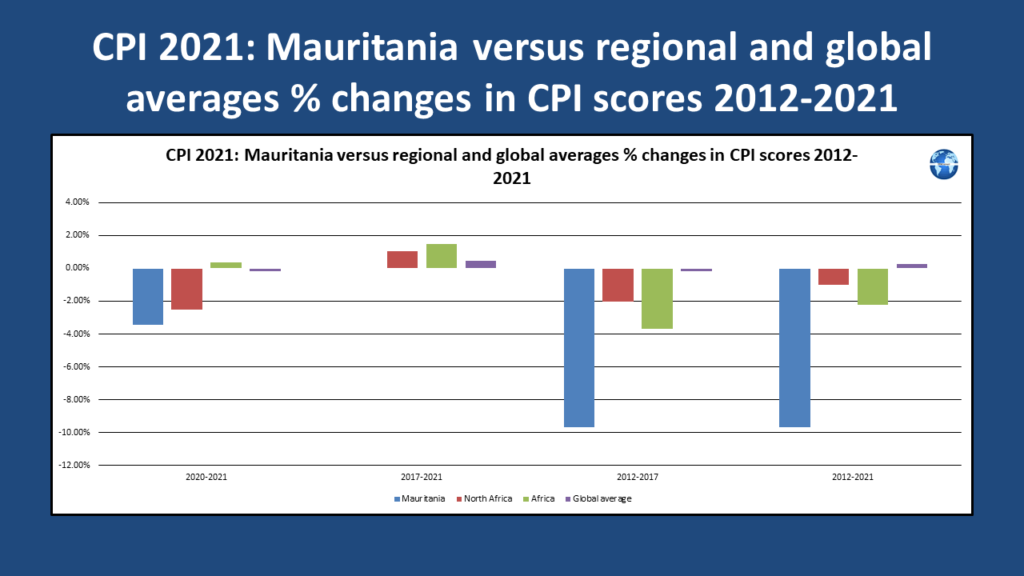
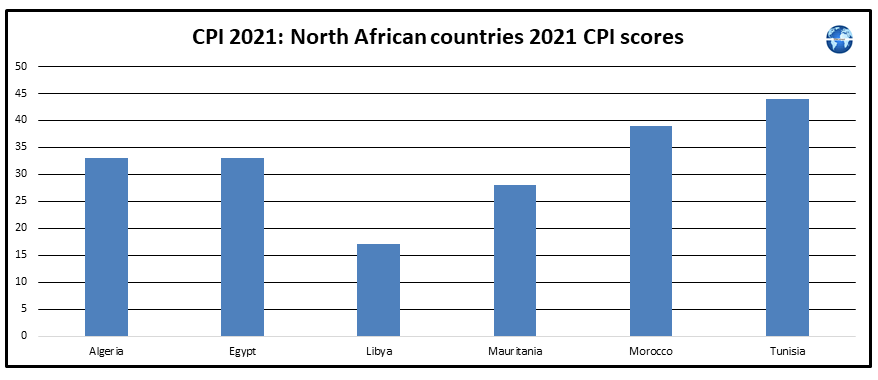
Scores for North African countries published by Transparency International in their 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) report demonstrate that North Africa was ranked first out of the five African regions in terms of improvements in country CPI scores during 2012-2021. Individual country CPI score performance was mixed for North African countries in the 2012-2021 period. The country reports for North African countries reveal that no North African country was effectively implementing current criminal penalties for corruption by officials. Further discussion on corruption trends in North African countries is provided here.
Details of the overview comments for North African countries in the 2021 country reports are provided below.
“Authorities continued their anticorruption campaign against political, military, and security officials, as well as prominent business leaders from the Bouteflika era.
The law provides for criminal penalties of two to 10 years in prison for official corruption, but the government did not fully implement the law. Although President Tebboune’s administration has emphasized rooting out corruption, corruption remained a problem. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but the government did not consistently implement the law effectively. There were reports of government corruption during the year, sometimes with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for official corruption. The government did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption but, as in 2020, no significant investigations or prosecutions occurred. There were many reports and accusations of government corruption due to the lack of transparency in the GNU’s management of security forces, oil revenues, and the national economy. There were allegations that government officials sometimes misused the letter of credit system to gain access to government funds.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by government officials, but authorities did not enforce the law effectively, and officials often engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but the government generally did not implement the law effectively. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were reports of government corruption in the executive, judicial, and legislative branches during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but the government generally did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.”
Conclusion
The country reports for North African countries demonstrate that no North African country is well placed to fight against corruption by officials due to material weaknesses in prosecution capacity.
Progress in combatting public sector corruption in North Africa is likely to be constrained until there is a considerable improvement in the relevant authorities’ ability to effectively enforce criminal penalties for corruption.