Corruption in Central Africa (a US perspective)
Introduction
The United States State Department’s Country Reports on Human Rights Practices (“country reports”) strive to provide a factual and objective record on the status of human rights worldwide. The 2021 country reports were published on 12 April 2022.
Section 4 of the country reports provides an assessment of Corruption and Lack of Transparency in Government which addresses the extent to which a country’s law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials and the level of implementation of these laws.
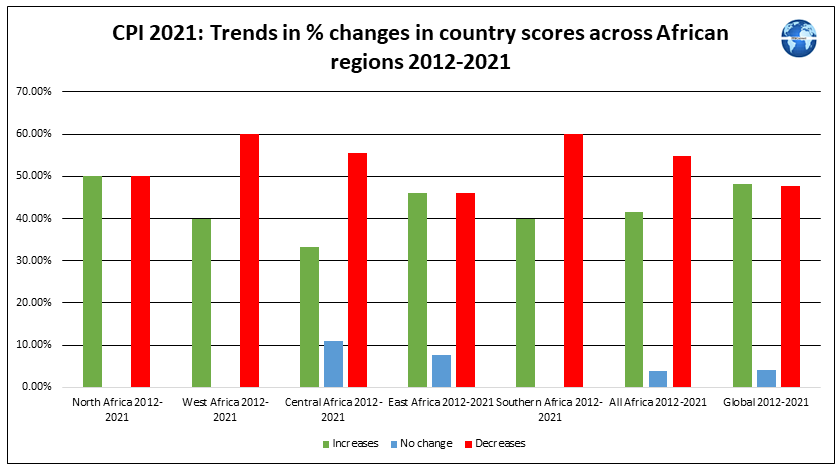
Scores for Central African countries published by Transparency International in their 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) report demonstrate that Central Africa has been the worst performing African region in terms of improvements in CPI scores during 2012-2021. It is not therefore surprising that the country reports for Central African countries reveal shortcomings in all Central African countries in the implementation of current criminal penalties for corruption by officials. Further discussion on corruption trends in Central African countries is provided here.
Details of the overview comments for Central African countries in the 2021 country reports are provided below.
“The law provides criminal penalties for official corruption, but the government did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year. Some high-level government officials engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. The constitution provides for the establishment of a High Court of Justice to review accusations of serious crimes against high-ranking government officials, but the court does not yet exist. The anticorruption law also applies to all other citizens, but no high-ranking official to date has stood trial for corruption.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but the government did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. The law identifies different offenses as corruption, including influence peddling, involvement in a prohibited employment, and failure to declare a known conflict of interest. Reporting corruption was encouraged through exempting whistleblowers from criminal proceedings. In addition to the laws, the National Anticorruption Agency (CONAC), Special Criminal Court, National Financial Investigation Agency, Ministry in Charge of Supreme State Audit, and Audit Bench of the Supreme Court also contributed to fighting corruption in the country. CONAC, the most prominent of the anticorruption agencies, was constrained by the absence of any legislative or presidential mandate that could empower it to combat corruption. There were reports that senior officials sentenced to prison were not always required to forfeit their ill-gotten gains.”
“Although the law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, the government did not effectively implement the law, and officials often engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. Corruption and nepotism have long been pervasive in all branches of government. Weak government capacity further limited attempts to address fully the problem of public-sector corruption. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but authorities did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.
According to Freedom House’s Freedom in The World 2021 report, corruption, bribery, and nepotism were “endemic” in the country, and prominent journalists, labor leaders, and religious figures faced harsh reprisals for speaking out concerning corruption, including arrest, prosecution, and exile.”
“The law provides for criminal penalties for corruption by officials. The government did not apply the anticorruption law, however, and many officials engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were some reports of government corruption during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, but the government did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year, and officials frequently engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. Local NGOs blamed these levels of corruption, in part, to the lack of a law providing for access to public information.
In 2020 President Tshisekedi created the Agency for the Prevention and Fight against Corruption (APLC). A special service under the Office of the President, the APLC is responsible for coordinating all government entities charged with fighting corruption and money laundering, conducting investigations with the full authority of judicial police, and overseeing transfer of public corruption cases to appropriate judicial authorities. The Platform for the Protection for Whistleblowers in Africa asserted that APLC’s record was mixed, without visible results.”
“While the law provides severe criminal penalties for official corruption, the government did not effectively implement the law. There are no specific laws concerning conflict of interest or nepotism. On May 10, the government passed an anticorruption measure, Law No. 1/2021, imposing stricter standards of behavior on public officials regarding their interactions with the formal and informal private sector.
Officials frequently engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were numerous reports of government corruption. The president and members of his inner circle continued to amass personal fortunes from the revenues associated with monopolies on all domestic commercial ventures, as well as timber and oil exports. Corruption at all levels of government was a severe problem.
According to Freedom House, the budget process was “opaque.” The government continued to improve fiscal transparency, including auditing state-owned enterprises and public debt using international accounting firms and publishing data on public-sector debt in the budget.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of corruption by officials, but the government did not implement the law effectively. There were isolated new reports of government corruption during the year. According to media and NGOs, officials frequently engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of official corruption, but the government generally did not implement the law effectively. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.”
Conclusion
The country reports for Central African countries demonstrate that the fight against corruption is far more than passing anti-corruption legislation. Criminal penalties for corruption by officials must be enforced if significant progress is to made in addressing corruption.