Corruption in Southern Africa (a US perspective)
Introduction
The United States State Department’s Country Reports on Human Rights Practices (“country reports”) strive to provide a factual and objective record on the status of human rights worldwide. The 2021 country reports were published on 12 April 2022.
Section 4 of the country reports provides an assessment of Corruption and Lack of Transparency in Government which addresses the extent to which a country’s law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials and the level of implementation of these laws.
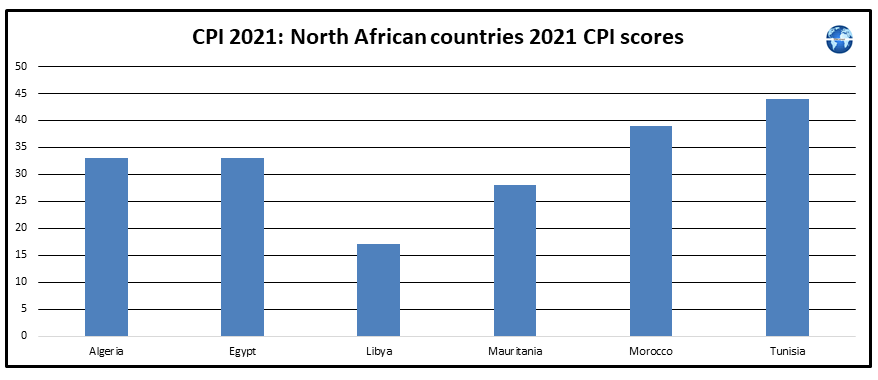
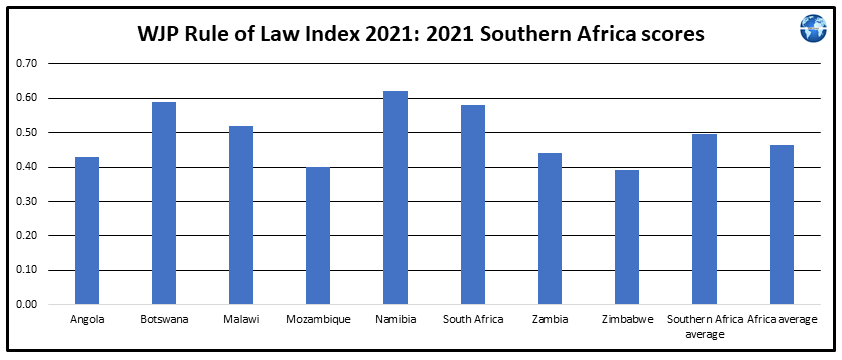
Scores for Southern African countries published by Transparency International in their 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) report demonstrate that Southern Africa was ranked second out of the five African regions in terms of improvements in CPI scores during 2012-2021. Individual country CPI score performance was mixed for Southern African countries in the 2012-2021 period. The country reports for Southern African countries reveal that only two Southern African countries were effectively implementing current criminal penalties for corruption by officials. Further discussion on corruption trends in Southern African countries is provided here.
Details of the overview comments for Southern African countries in the 2021 country reports are provided below.
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, and the government implemented the law effectively. The government dismissed and prosecuted cabinet ministers, provincial governors, senior military officers, and other officials for corruption and financial crimes. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year. The Attorney General’s Office continued corruption investigations and brought criminal charges against several officials. Nonetheless, official impunity and the uniform application of anticorruption legislation remained a serious problem.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, and the government generally sought to implement these laws effectively. Officials tasked with enforcement lacked adequate training and resources, however. Media reports of government corruption continued. During the year there were numerous reports of government corruption, including allegations tied to tenders issued by local governments for COVID-19 projects, such as renovating public facilities so that they complied with virus prevention measures, as well as in the acquisition of personal protective equipment. A 2019 poll by Transparency International found that 7 percent of those polled had paid bribes to government officials, an increase from the 1 percent who reported paying bribes in a 2015 poll.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for corruption by officials, and the government generally implemented the law effectively. There were isolated reports of government corruption during the year. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of corruption by officials. The government did not implement the law effectively, and some officials engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of corruption by officials, but the government did not implement the law effectively. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.
The government, in cooperation with donors, continued implementation of an action plan to pursue cases of corruption, reviewed how the “Cashgate” corruption scandal occurred, and introduced internal controls and improved systems to prevent further occurrences. Progress on investigations and promised reforms was slow.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of corrupt acts by officials; however, the government did not implement the law effectively, and officials often engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were numerous reports of corruption in all branches and at all levels of government during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of official corruption; however, the government did not implement the law effectively. Officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides for criminal penalties for conviction of official corruption, and the government generally did not implement the law effectively, and officials sometimes engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. There were numerous reports of government corruption during the year.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for officials convicted of corruption, and the government attempted to enforce the law but did so inconsistently. Officials often engaged in corrupt practices with impunity. Although the government collaborated with the international community and civil society organizations to improve capacity to investigate and prevent corruption, anticorruption NGOs observed that, the enforcement rate was low among senior government officials and in the civil service.
According to Transparency International Zambia, the conviction rate for those prosecuted for corruption was 10 to 20 percent. The Patriotic Front government did not effectively or consistently apply laws against corrupt officials; it selectively applied anticorruption law to target opposition leaders or officials who ran afoul of it. Transparency International Zambia further reported that, during the Patriotic Front administration, officials frequently engaged in corrupt practices with impunity.”
“The law provides criminal penalties for conviction of corruption; however, the government did not implement the law effectively or impartially. Despite government pronouncements, there were numerous reports of government corruption during the year. Experts described the problem as “catch and release,” where the government arrested some corrupt officials, often those out of favour, without ever convicting them.”
Conclusion
The country reports for Southern African countries demonstrate that only a minority of these countries are currently well placed to fight against corruption by officials. It is interesting to note that Angola and Eswatini which recorded relatively low scores in the 2021 Corruptions Perceptions Index were assessed in the country reports as enforcing criminal penalties for corruption relatively effectively.
Significant challenges in combatting corruption in Southern Africa are likely to remain until such time as the majority of countries make significant improvement in their ability to enforce criminal penalties for corruption.